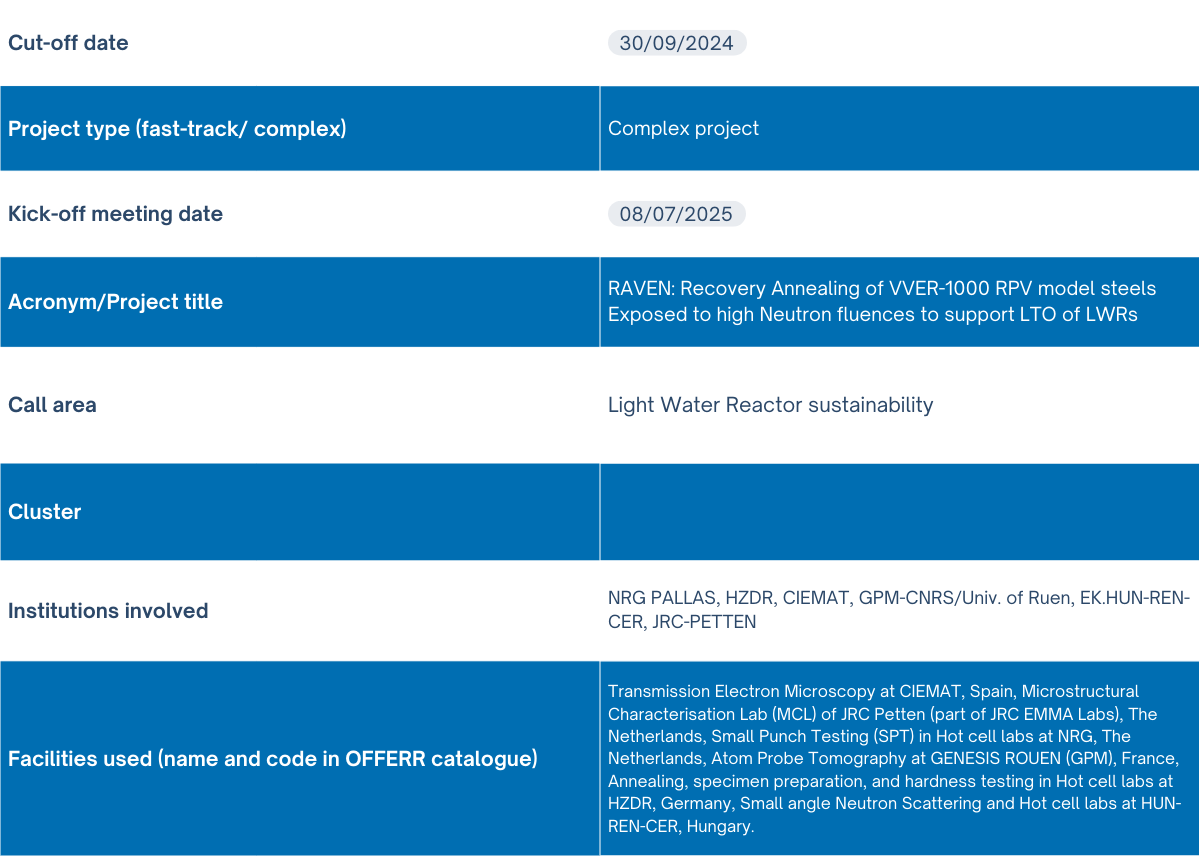
RAVEN Project
What is RAVEN?
The RAVEN project aims to investigate post-irradiation annealing (PIA) as a mitigation strategy for embrittlement in VVER-1000 reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels, supporting the long-term operation (LTO) of light water reactors (LWRs). Embrittlement of RPVs due to neutron irradiation is a critical issue for LTO, potentially leading to reactor shutdown if mechanical properties degrade beyond safe operational limits.
While PIA has successfully extended the life of high-Cu VVER-440 RPVs, its application to low-Cu VVER-1000 and European PWR reactors has been limited due to insufficient data on the behavior of Mn-Ni-Si clusters, which are primarily responsible for embrittlement in these steels. Building on the findings from the STRUMAT-LTO project, RAVEN will focus on characterizing the microstructural evolution of VVER-1000 steels subjected to PIA at temperatures ranging from 400-475°C. The project will examine the dissolution of Mn-Ni-Si clusters, believed to drive the recovery of mechanical properties. Comprehensive microstructural analysis will correlate these changes with mechanical testing data, including tensile, hardness, and small punch tests (SPT). The goal is to confirm PIA as a viable strategy for recovering the mechanical properties of low-Cu RPV steels irradiated to high fluences, thereby supporting the safe, extended operation of European VVER-1000 reactors.
Objectives
The main objective of this study is to investigate the thermal stability of different types of radiation induced defects in VVER-1000 PRV steels, and their roles on the recovery of mechanical properties after post-irradiation annealing. This objective will be achieved by performing detailed microstructural characterization of selected RPV steels, submitted to different PIA treatments, using complementary techniques and correlating the microstructural data to mechanical properties (e.g. tensile, hardness and SPT). Tensile data obtained from STRUMAT-LTO project, which is a recently finished H2020 project, will be used in addition to hardness and SPT testing proposed here. In addition, the PIA microstructure is the starting point for future investigation of the re-irradiation behavior of VVER-1000 RPV steels, which is still lacking in literature and is needed for commercial application of this mitigation technique on VVER-1000 reactors.
Main outcomes
The project strated recebtly. Currently 2 material transport from NRG to CIEMAT and CNRS finished. Sample preparation for microscopy and and mechncial testing are planned in Q4 2025.


Publications
No publications yet.
Interest for use of reached results
All LTO stakeholders





